Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck was born on 1 April 1815 on the family estate of Schönhausen west of Berlin in the Prussian province of Saxony. His father was Ferdinand von Bismarck, landowner and a former Prussian military officer, and his mother was Wilhelmine Mencken who had come from a relatively well-off commoner family. Bismarck had several siblings, but only his elder brother and younger sister survived to the adult age. His family had been nobles since the fourteenth century, and since his birth Bismarck held the title of Graf (Count).
Bismarck was educated at fine Prussian secondary schools and studied at the University of Göttingen and then at the University of Berlin. Bismarck hoped to become a diplomat and started his practical training as a lawyer in Aachen and Potsdam. He resigned soon after, partly because of a scandal involving his pursuit of two English women. In 1847, Bismarck married Johanna von Puttkamer with whom he had 3 children.
Bismarck was elected to the Prussian Diet in 1849, and then two years later he became the Prussian representative to the federal diet in Frankfurt. In both offices, Bismarck displayed his staunch support of the Prussian monarchy. And it was during those first years in politics that Bismarck saw first-hand the failure of German liberals to unify Germany during the unrest of 1848-50. This further convinced him of the need for the Prussian king to unify Germany. Bismarck next held the important diplomatic posts of first Prussian ambassador to Russia and then ambassador to France. This would give Bismarck important diplomatic connections abroad and within Germany that he could use during the process of German unification.
In the late 1850s, Prussian King Frederick William IV was succeeded by his brother, William I, as regent (1858-61) and then as king (1861-88). Aroused by the uncertain state of international affairs in 1859, William sought to reform and enlarge the Prussian army. Liberals in the Prussian Landtag, opposing the military build-up, claimed the legal right to control expenditures, whereas the king, as head of the army, claimed the right to institute military reforms and to require the necessary funds be appropriated. A political deadlock arose for which the Prussian constitution had no provision. The king considered abdication, but finally fell back upon Prince Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898) to break the deadlock. Bismarck already had a reputation as a conservative, an anti-parliamentarian, a nationalist, and a man of intelligence.
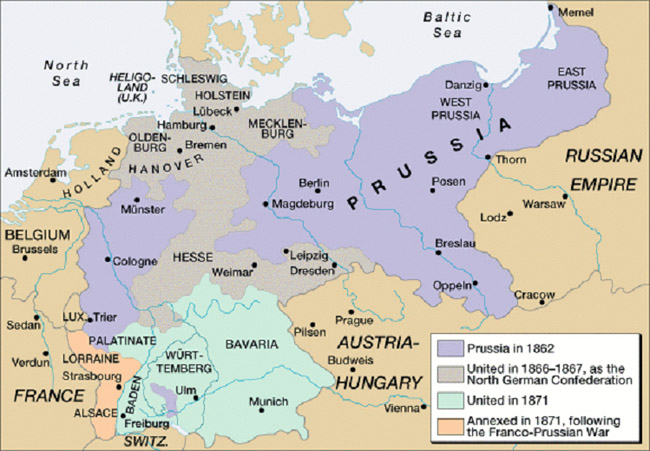
In September 1862 Bismarck became the prime minister and foreign minister of Prussia, which, at the time, was considered the weakest of the major European powers. But under Bismarck’s skillful leadership, Prussia was able to achieve the goal of political unification of a Prussian dominated German Empire. This culminated with the announcement of the establishment of the German Empire on 18 January 1871 in the Hall of Mirrors in the Château de Versailles. Bismarck became chancellor of Germany.
In the years after 1871, Bismarck skillfully worked to preserve the peace in Europe through a complex set of alliances designed to isolate France. Domestically, he introduced administrative and economic reforms, including a set of far reaching social security insurance programs, while still trying to preserve the social status quo, i.e., the power of the conservative, Prussian nobility.
After a dispute with the new German emperor, Bismarck left office in 1890 with the map of Europe greatly changed immeasurably. In retirement, he turned to the writing of his memoirs.
Some quotes attributed to Bismarck
- "A statesman... must wait until he hears the steps of God sounding through events, then leap up and grasp the hem of His garment."
- "The Americans have contrived to be surrounded on two sides by weak neighbors and on two sides - by fish!"
- "Anyone who has ever looked into the glazed eyes of a soldier dying on the battlefield will think hard before starting a war."
- “History is simply a piece of paper covered with print; the main thing is still to make history, not to write it.”
- "I am bored; all of the great things have been done."
- "The Balkans starts in the slums of Vienna."
- "The world spins around in circles. Germany remains stagnant."
- "Politics is the art of the possible."
- "Not by speeches and majority votes are the great questions of the day decided - that was the great error of 1848 and 1849 - but by blood and iron."
- "People never lie so much as after a hunt, during a war or before an election"
Some recommended online lectures and websites
- We have available in the course, an old map of Prussia (*.PDF) provided by a former student, Eleanore Tutwiler.
- Bismarck's Revelations, this is actually a book review of Bismarck's Memoirs, published in the New York Times (4 December 1892)
- The Reinsurance Treaty (18 June 1887) between Germany and Russia
- Otto von Bismarck & German Unification; there is also biographical information at Germanculture.com
- Bismarck in Wikipedia (See also the entry for the German Empire.)
- Otto von Bismarck and Social Security (brief note)
- Bismarck’s Foreign Policy 1871-1890, a brief summary; see also Bismarck and Unification, or Country-data.com; or The Life of Otto von Bismarck
- James Graham, Was Bismarck the Key Factor in the Unification of Germany?
- Volume 2 of Bismarck’s memoirs are available in English; Bismarck, the man and the statesman; being the reflections and reminiscences of Otto, Prince von Bismarck (1898)
- There are many documentary collections available online, including The correspondence of William I. and Bismarck : with other letters from and to Prince Bismarck.. If you are really brave, you can tackle volume 1 or volume 2 of Gedanken und Erinnerungen by Bismarck
- For extra credit please suggest to your instructor a relevant website for this unit of the course. Send the title of the site, the URL and a brief explanation why you find the information interesting and applicable to the material being studied in this unit.